In English, ‘Utility’ is best translated as ‘useful’ or ‘something that is useful or profitable’. In a more free translation of utility in the application to NFTs: “what benefit does it bring me” and “what else do I get if I buy that NFT?”. In a more general sense, utility in an NFT refers to the values, benefits or rewards that an NFT offers to its buyers and holders. The most obvious utility that an NFT can provide is the digital ownership of a digital asset. However, the utility of NFTs can be quickly extended in both the digital and physical worlds by linking NFTs to e.g. membership, discount, ticket, intellectual property, and copyright or by linking them to DeFi – Decentralized Finance – projects as an asset and physical collectibles in the broadest sense.
Utility NFTs are therefore regular Non Fungible Tokens that provide more than just the piece of code on the Blockchain. The owner of the NFT can prove (through ownership) that he or she is entitled to the benefits and values that belong to that particular NFT.
Examples of Utility NFTs
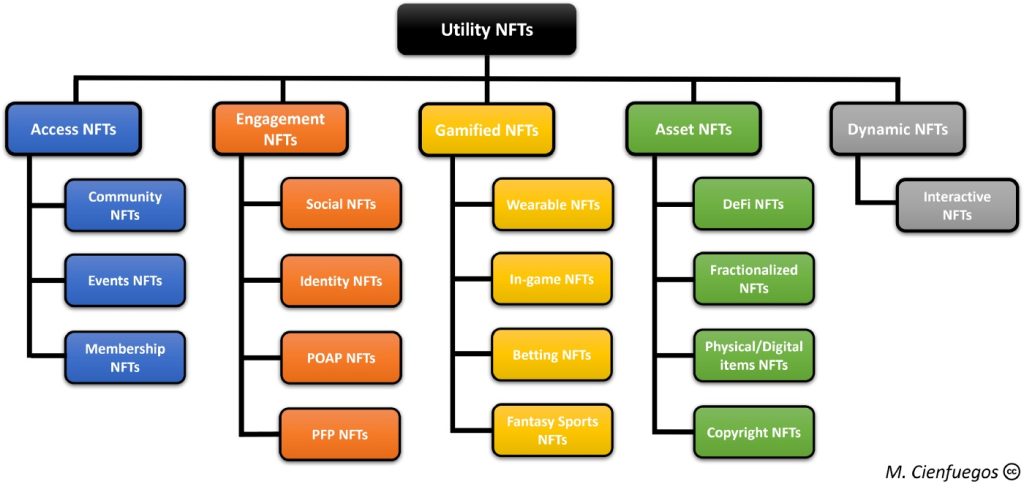
Access NFTs
Give their owners access to communities, events, or experiences in both the digital and physical world.
Community NFTs
provide exclusive access to members-only channels such as Discord channels or various types of content stored on other platforms, such as blogs, NFT-gated websites, or the metaverse, where only NFT owners from the community are allowed. It is common for creators to organise meetups and parties for their community members; all this increases the value of the project and makes it worth owning.
Events NFTs
are among the most popular use cases for Access NFTs, with different companies implementing different protocols to use them. They provide access to real life experiences, both online and offline. One of the most common types is NFT-based tickets, where the NFT keeps track of your access details for a specific event.
Membership NFTs
give holders access to exclusive programmes that use NFTs as access keys to unlock various services and rewards. These can range from discounts on merchandise, free access to events, or new product drops. Projects and brands can sometimes allow their NFT holders to participate in voting.
2. Engagement NFTs
Engagement NFTs
are used to connect with brands and other users in the community. Collectibles usually fall into this category as well. The Bored Apes Yacht Club (BAYC) became a famous example of engagement NFTs, which are used on various social media platforms and are considered by many to be a digital symbol of social status. The company behind the BAYC collection, Yuga Labs, has announced the project ‘Otherside’ in which they bring the Bored Apes into the metaverse as characters in the form of NFTs.
Social NFTs
can be used socially in the form of badges, emblems, GIFs and emojis that can be used in social context and social platforms and are available to be used within that community or across 3D worlds.
Identity NFTs
allow individuals to display and have an identity across platforms that they can use in different ecosystems in the form of avatars or interactable characters.
POAP NFTs
– Proof of Attendance Protocol (POAP) – NFTs are used by communities and brands to prove that they have been to an event or experience that took place virtually or in the real world. Some institutions also use them to issue digital certificates upon successful completion of a programme.
PFP NFTs
– Profile Picture (PFP) – NFTs are typically collections designed to be used as profile pictures in social media. Their popularity has helped them to be adopted not only into the NFT communities, but also by celebrities and businesses around the world.
3. Gamefied NFTs
NFTs with a specific set of elements that are part of the activities in a game universe and can be bought and sold on external peer-to-peer marketplaces.
Wearable NFTs
are usually virtual items of clothing or digital accessories such as dresses, shirts, jeans, sunglasses or bags that allow you to dress your avatar in a virtual world. They also refer to Augmented Reality (AR) filters, which are clothes or accessories that are only visible in augmented reality, and can be worn in the “real world”.
In-game NFTs
also known as Play-To-Earn NFTs, provide gamers with special characters, skills, weapons and various other in-game items that can later be used as assets to generate income by trading them to other players or collectors or by keeping them as a form of passive income.
Betting NFTs
are used to boost online betting by offering their owners additional bonuses and benefits at specific betting and gaming sites.
Phantasy Sports NFTs
are fantasy sports trading cards that can be traded and used in various Online gaming platforms and gamified scenarios.
4. Assets NFTs
Includes ownership of a unique, value-based digital or physical asset that can be sold, leased, licensed, or transferred to other users.
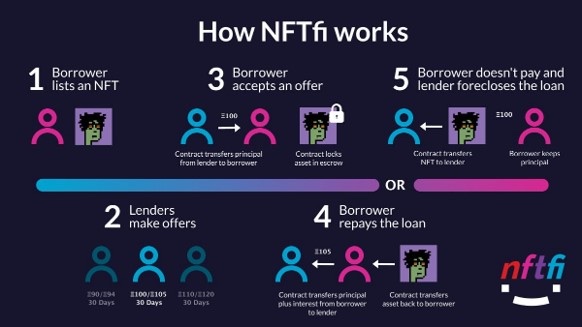
A new trend in the development of this is the intersection of NFTs and DeFi. This combination has opened up several possibilities for NFT holders by making their NFTs a much more liquid asset – in a safe, secure and anonymous way. NFTfi is an excellent example of this type of NFT. Image rights belong to NFTfi.
DeFi NFTs
This new category of NFTs is linked to DeFi schemes and ecosystems that allow owners to deploy, accumulate and collateralise NFTs to access the liquidity they need or to efficiently make attractive profits through various DeFi mechanisms.
Fractionalized NFTs
have the ability to divide the ownership of an NFT into smaller fractions and allow owners to fragment their NFTs and sell fractionalised shares. They also make it possible to collectively buy an NFT that would otherwise be difficult to buy because of its high price.
Physical/digital NFTs
are associated with the ownership of physical and/or digital assets. They act as a property guarantee over real, physical or digital off-chain assets and items that the buyer can exchange.
Copyright NFTs
grant ownership of copyrights and imply a transfer of trademark rights or licenses to the item to which the NFT is attached. This gives NFT holders commercial usage rights to their NFTs and in some cases includes sublicensing rights. All rights given end automatically when the NFT is sold.
5. Dynamic NFTs
Dynamic NFTs typically involve some form of metadata change that is encoded in the NFT smart contract based on external conditions. The smart contract gives instructions to the underlying NFT on when and how the metadata should change. The changes can also be triggered by specific user interactions outside the chain. This functionality can be useful for character progression to reflect character growth, but also in the tokenization of real-world assets, where changes in the asset change along with changes in the metadata. The metadata of Dynamic NFT representing a property can change to reflect maintenance history, past sales, and details. Image rights belong to Chainlink.
Interactive NFTs
have the ability to interact with the holder or with another set of actions within an environment that cause changes in the attributes and characteristics.
Some of the practical benefits that Utility NFTs can offer
Exclusive parties and events
It is a trend of the last few years, certain parties and events are only getting more exclusive and the advent of Non-Fungible Tokens (and the Blockchain) has added to this. Because of the certificate behind unique NFT’s, it’s quite easy to show who is welcome at a certain event or exclusive VIP party and who is not.
Membership
Think of a gym membership, or a separate space within a certain gym. Here again, the term exclusivity is very appropriate.
Upgrade hotel room
It is not unthinkable – if it doesn’t happen already – that at some hotels you will be offered a free upgrade if you are in possession of the certificate of a certain NFT. If this is a hotel chain with hotels all over the world, this can be a real advantage.
NFT Games
In addition to gaining access to certain NFT Game, you may also be given a number of benefits (during a battle or the option of managing an exclusive character).
Earlier, we mentioned the Bored Ape Yacht Club as an NFT that brings several perks. Currently, however, you need to have very deep pockets to get such an NFT. Fortunately, there are other projects that can provide more than just the digital certificate:
Axie Infinity NFT Game and these give you a lot more than just the certificate. You can get access to the exclusive Axie Infinity Discord and the Mavis Hub Community. In addition, you can also get extras within the game, where you can get certain items that are otherwise very expensive to obtain.
Moon Boys series is constantly working to add more value to its NFTs, which are for sale on Opensea. The 3D designed NFTs give access to the Moon Boys Party Platform and there it is possible to get certain merchandise. Moon Boys also has a VIP club, obviously only for certificate holders.
Concluding thoughts
The given classification of NFTs is not complete or definitive. The Utility NFT ecosystem is constantly growing, and new use cases will continue to emerge in many industries. Innovators, experts and organisations have a prime opportunity to determine the paths they take to provide NFTs with more meaningful utilities. However, it is up to the entire ecosystem, including holders, to assess and decide which NFTs to buy and hold for the long term. It is likely that future NFTs will include trends of increasingly innovative utilities, as well as a combination of different types of them.
The options are endless. Both within the Blockchain and NFT world and outside it, there are examples of how Utility NFTs can bring you all kinds of benefits. And these possibilities will probably only grow, as will the value of the NFTs in question.
If you are interested in what Utility NFTs can bring to you or your business, please contact us. We are experts in the development of NFT applications and are happy to help you with ideas and advice. All our solutions are realised on the Concordium first Layer-1 blockchain with ID-framework and are therefore ideally suited for applications in regulated or closed markets where KYC, AML and GDPR legislation is required.



0 Comments